Dental Cleaning
Periodontal Gum Surgery & Gum Treatment in Pune
All Services
In India, gum disease is highly prevalent, affecting up to three out of every ten adults, resulting in varying degrees of moderate to severe gum issues.
Neglecting gum disease can lead to discomfort and significant harm to both your oral health and overall well-being. Therefore, it’s crucial to take proactive measures to prevent its onset and promptly address it if it emerges, in order to prevent potential complications. This proactive approach will contribute to maintaining a vibrant and contented smile, allowing you to continue with your daily life.
Should you experience advanced gum disease (referred to as periodontal disease), your dentist might recommend considering gum surgery as a potential treatment option.

What is gum disease?
Gum disease, medically termed periodontitis, refers to an infection that affects the gums and the surrounding tissues of your teeth. It presents in two primary forms: gingivitis and periodontitis.
Gingivitis is the more prevalent and less severe variant. It manifests as redness and swelling of the gums, occasionally accompanied by minor bleeding during tooth brushing. The encouraging news is that diligent oral care practices such as brushing and flossing can reverse gingivitis, restoring a healthy smile.
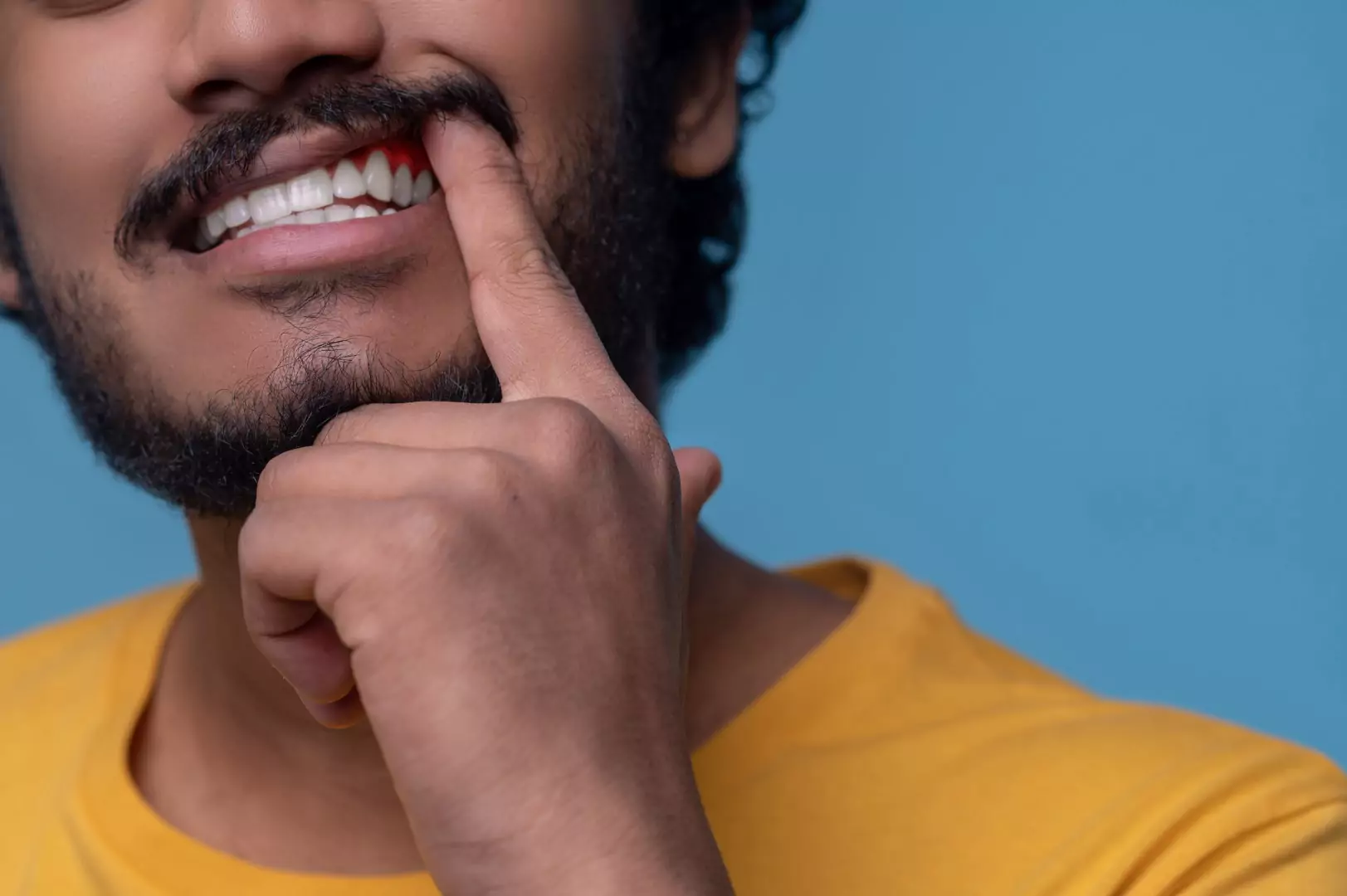

The second variation is periodontitis, which can be considered an advanced stage of gingivitis. Periodontitis develops when untreated gingivitis progresses, potentially leading to significant complications. During this stage, the inflammation and infection of the gums seen in gingivitis worsen, extending to the point where the underlying bone can also be affected. Over time, substantial bone loss might occur, resulting in tooth mobility, discomfort, and the potential need for extraction.
Regrettably, periodontitis cannot be entirely cured; its effects can only be managed. As a result, preventing gingivitis from reaching this critical stage is of paramount importance.
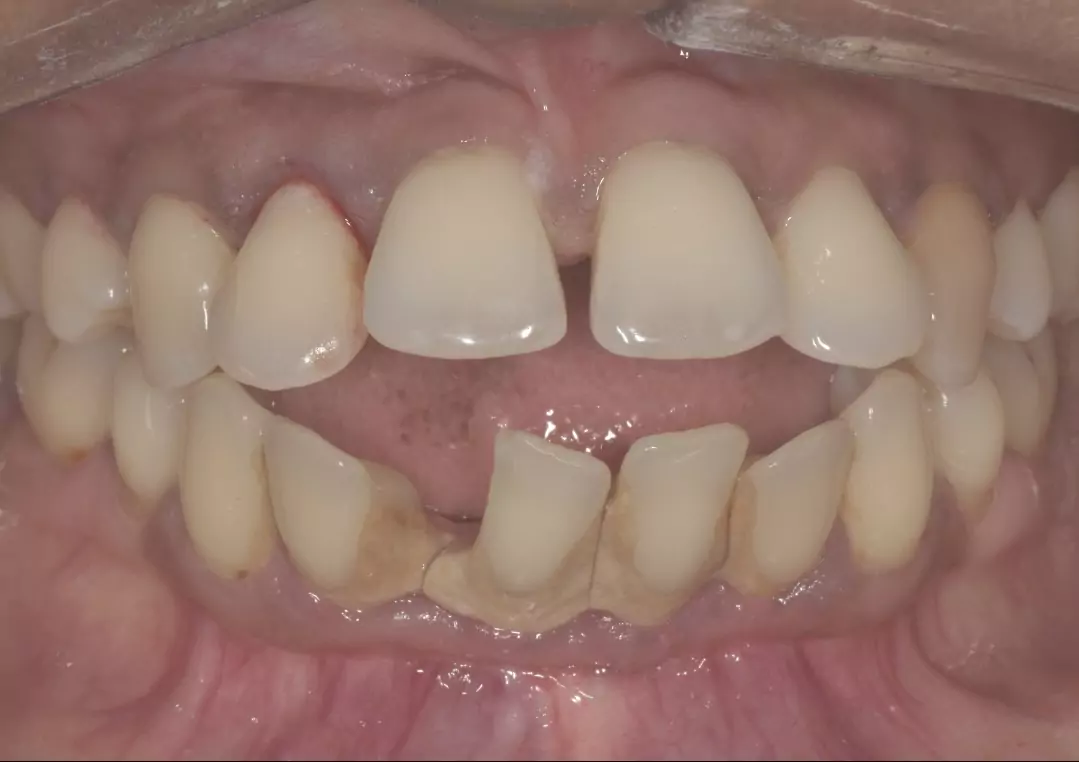
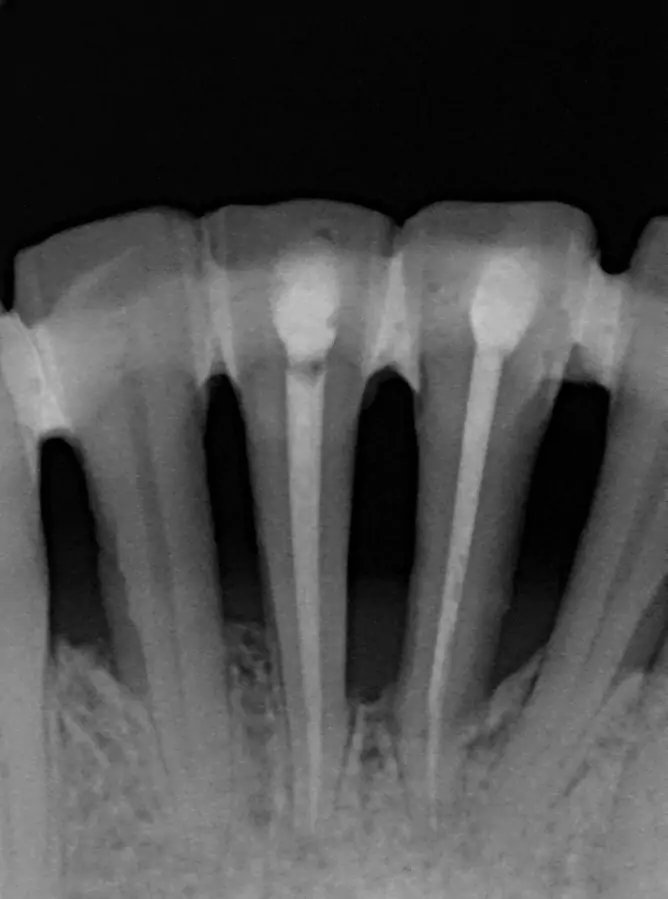
What triggers gum disease?
Both types of gum disease frequently originate from inadequate oral hygiene practices, resulting in the accumulation of plaque on the teeth. Plaque, formed by bacteria, adheres to teeth and necessitates thorough brushing and flossing for its removal. If oral care is insufficient or infrequent, the accumulated plaque can begin to irritate the gums. Over time, it solidifies into a substance called tartar, which can only be removed by a dental professional. Tartar is even more detrimental to the gums than plaque, perpetuating irritation and exacerbating gum disease.
Nevertheless, there exist various factors that can contribute to the development of gingivitis and periodontitis. These factors encompass:
- Inadequate or irregular brushing and flossing routines
- Unhealthy dietary habits, including excessive sugar consumption
- Smoking and substance abuse
- Certain medications
- Diabetes and other medical conditions
- Genetic predisposition
- Puberty
- Pregnancy
Your dentist can assist in identifying the underlying cause of your gum disease, aiding you in taking preventive or management measures.

How can I determine if I am affected by gum disease?
In many instances, you might observe your gums bleeding while brushing. Even a slight amount of blood when rinsing can often indicate the presence of gingivitis. On closer examination, you might also notice that your gums appear red and inflamed.
Nonetheless, it’s possible that your dentist could be the first to identify gum disease during a routine dental examination. While assessing your teeth is customary, dentists also pay attention to your gums and tongue, looking for any irregularities or signs of disease. They will then recommend immediate measures to address the issue.
If you suspect gum disease, it’s crucial to promptly adopt effective oral hygiene practices such as brushing and flossing twice daily, in addition to minimising your intake of sugary foods and drinks. Additionally, reach out to your dentist for guidance, as they might advise you to schedule a check-up and professional dental cleaning. This proactive step can help mitigate the issue before it potentially worsens.
How does the treatment for gum disease function?
If you’re dealing with gingivitis, there’s good news: improving your oral hygiene habits through regular brushing, flossing, and adopting a healthier diet might be all that’s necessary. Your dentist might also recommend a professional cleaning session to remove any accumulated plaque.
However, when it comes to periodontitis, a condition that isn’t curable, the focus shifts to managing symptoms and preventing further deterioration.
Typically, the initial approach for treating periodontitis involves a thorough and deep cleaning. Often performed under anaesthesia due to potential discomfort, this process targets the areas below the gumline.
Should this initial treatment not yield desired results, the next step is often gum surgery. This surgical procedure aims to address or eliminate the spaces that develop between your teeth and gums as a result of bone loss.
During the surgery, your dentist or periodontist will create small incisions in your gum tissue to create a flap, providing access to the infected area. The affected gum tissue will be removed, and tooth-scaling and root-planing techniques will be employed to eliminate any plaque or bacteria below the gum line.
Subsequently, the gums will be repositioned and secured using dissolvable stitches. A follow-up appointment, scheduled for 7-10 days later, will allow your dental professional to assess your healing progress.
This surgery is conducted under local anaesthesia by a dentist, depending on the specific procedure. It’s essential to inform your dentist about any current medications or health conditions, as these factors might influence the recommended approach.



